- Understanding the Psychology Behind Impulse Buying
- The Influence of Psychological Factors on Impulse Buying
- Understanding the Impulse Buying Behavior
- The Role of Emotions in Impulse Buying
- The Impact of Cognitive Biases on Impulse Buying
- The Role of Social Interactions in Impulse Buying
- The Effect of Advertising and Marketing Strategies on Impulse Buying
- The Influence of Store Layout and Design on Impulse Buying
- The Relationship Between Impulse Buying and Self-Control
- Impulse Buying as a Form of Instant Gratification
- The Link Between Impulse Buying and Consumer Satisfaction
- The Connection Between Impulse Buying and Retail Therapy
- The Psychological Consequences of Impulse Buying
- Strategies to Resist Impulse Buying
Understanding the Psychology Behind Impulse Buying
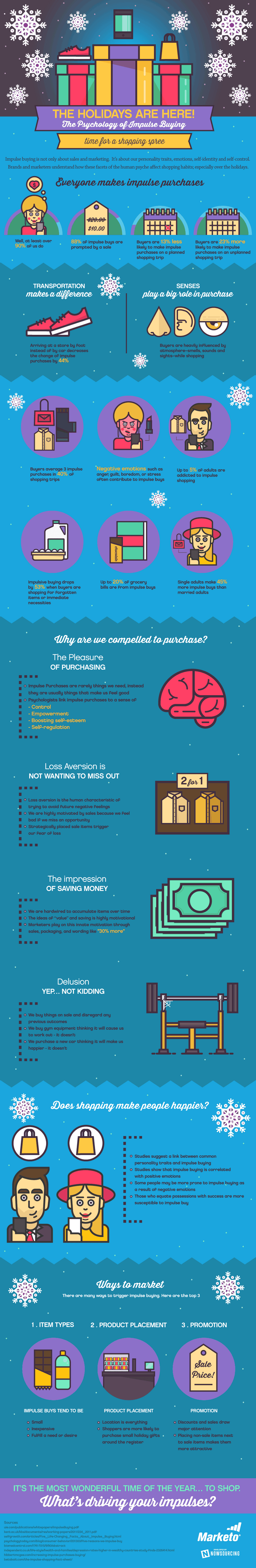
In today’s consumer-driven society, shopping has become more than just a necessity; it has evolved into an experience. The fascinating world of shopping psychology reveals the intricate and subconscious factors that influence our purchase decisions. One such phenomenon is impulse buying, a psychological impulse that drives us to make immediate, unplanned purchases.
Emotional shopping plays a significant role in impulse buying. As consumers, we are often swayed by our emotions, seeking instant gratification and a boost in mood. Retailers, both in-store and online, capitalize on this by employing various strategies. Visual merchandising and product placement are carefully designed to create an appealing environment and entice us to make impulsive purchases. On the other hand, ecommerce platforms use price strategies and sales promotions to evoke a sense of urgency, further triggering impulsive behavior.
Consumer behavior in online shopping differs from in-store shopping but is equally influenced by impulse buying. While the lack of physical presence may seem to reduce impulsive tendencies, the ease and convenience of the online check-out process can actually amplify impulsive buying. Additionally, online retailers use sophisticated algorithms based on consumer research to tailor product recommendations, encouraging impulse purchases.
Retail marketing is constantly evolving, and understanding the psychology behind impulse buying is crucial in staying ahead of retail trends. Sales promotions, product packaging, and even the concept of retail therapy are all strategies employed by brands to appeal to our impulsive nature. By tapping into our emotions and understanding the desire for instant gratification, retailers can create a sense of urgency and ultimately drive more sales.
The Influence of Psychological Factors on Impulse Buying
Impulse buying is a common phenomenon in consumer behavior, and it is greatly influenced by various psychological factors. One important factor is visual merchandising, which involves the strategic arrangement of products in a way that attracts and tempts customers. Retailers use techniques such as color, lighting, and product placement to create an appealing environment that encourages impulse buying.
Emotional shopping is another psychological factor that affects impulse buying. Many people engage in retail therapy, using shopping as a way to alleviate stress or boost their mood. Retailers tap into this by offering a wide variety of products and creating a pleasant shopping experience to satisfy consumers’ emotional needs.
In-store shopping provides consumers with the opportunity to see and touch the products before making a purchase, which can trigger impulse buying. Furthermore, retailers use price strategies and sales promotions to make consumers feel like they are getting a good deal, which can influence impulse buying behavior.
Product packaging is also crucial in influencing impulse buying. Attractive and eye-catching packaging can grab consumers’ attention and make them more likely to purchase a product on impulse. Additionally, retailers use consumer research to understand their target audience and develop packaging that appeals to their desires and preferences.
The check-out process is another important factor in impulse buying. Retailers strategically place small, inexpensive items near the check-out counter to tempt consumers into making an additional impulse purchase. They also use suggestive selling techniques and offer special deals to encourage impulse buying during this critical moment.
With the rise of online shopping and ecommerce, retailers have adapted their strategies to influence impulse buying. They use techniques such as personalized recommendations, limited-time offers, and countdown timers to create a sense of urgency and encourage immediate purchase decisions.
Overall, understanding the psychology behind impulse buying is crucial for retailers in order to effectively engage customers and increase sales. By leveraging factors such as visual merchandising, emotional shopping, product packaging, and the check-out process, retailers can tap into consumers’ desire for instant gratification and capitalize on the trend of impulse buying.
Understanding the Impulse Buying Behavior
Impulse buying refers to the phenomenon where consumers make unplanned purchases on the spur of the moment, often driven by emotional factors. As a result, understanding and harnessing the psychology behind impulse buying behavior has become a crucial aspect of retail marketing and consumer research.
Retail trends and visual merchandising play a significant role in triggering impulse buying. Retailers strategically design their stores and product placements to attract consumers’ attention and leverage consumer behavior. Eye-catching displays, product packaging, and sales promotions can all contribute to the impulsive decision-making process.
In-store shopping experiences are often designed to create a sense of retail therapy, where consumers seek emotional gratification through their purchase decisions. This notion of instant gratification is a key driver of impulse buying, as consumers seek to fulfill their desires and feel a sense of pleasure or excitement.
While impulse buying has traditionally been associated with in-store shopping, the rise of online shopping has also caused a shift in the dynamics of impulse buying. E-commerce platforms utilize various strategies, such as targeted ads and personalized recommendations, to capitalize on impulse buying tendencies and facilitate seamless checkout processes.
Price strategy also plays a crucial role in impulse buying behavior. By offering limited-time discounts or exclusive deals, retailers tap into consumers’ fear of missing out and create a sense of urgency. This can further amplify the impulsive nature of purchase decisions.
In summary, impulse buying behavior is influenced by emotional factors, retail trends, visual merchandising, consumer behavior, product packaging, in-store shopping experiences, product placement, sales promotions, and price strategies. Understanding these factors and their effects on consumers’ decision-making process is vital for retailers and marketers looking to maximize their sales and engage with their target audience effectively.
The Role of Emotions in Impulse Buying
In the ever-evolving world of retail trends, impulse buying has become a significant driver of buying habits. Understanding the psychology behind impulse buying is crucial for retailers and marketers to create effective strategies that capitalize on consumers’ emotions.
Emotions play a pivotal role in impulse buying, as they can override rational decision-making and lead consumers to make unplanned purchases. Through consumer research, it has been identified that certain emotions, such as excitement, pleasure, and even stress, can trigger impulsivity in shopping behavior.
Price strategies and online shopping have both been proven to elicit emotional responses from consumers. The use of sales promotions and attractive discounts can create a sense of urgency, encouraging consumers to make impulsive purchases. In the realm of ecommerce, the convenience and instant gratification associated with online shopping can strengthen the emotional appeal of impulse buying.
Retail therapy, often driven by emotional needs, can heavily influence the check-out process and purchase decisions. The desire to seek emotional fulfillment through shopping can lead consumers to make impulsive purchases, as they seek instant gratification and a temporary escape from reality.
Visual merchandising and retail marketing techniques also tap into consumers’ emotions to encourage impulse buying. Effective product packaging, product placement, and appealing displays can trigger emotional responses, capturing consumers’ attention and enticing them to make impulsive purchases.
While online shopping has gained popularity in recent years, in-store shopping still provides ample opportunities for impulse buying. The sensory experiences of being in a physical store, such as touching, smelling, and trying on products, can evoke emotions that influence purchasing decisions.
In conclusion, emotions play a critical role in impulse buying. Understanding and leveraging consumers’ emotional responses through various retail strategies can effectively drive impulsive purchases and contribute to the success of businesses in today’s competitive market.
The Impact of Cognitive Biases on Impulse Buying
Consumer behavior in the realm of impulse buying is tremendously influenced by several cognitive biases. These biases dictate our shopping psychology, often leading to impulsive purchases both in brick-and-mortar stores and online.
In the world of ecommerce, retailers strategically leverage cognitive biases to boost sales. One such bias is the pricing strategy, where retailers use tactics like discounts, limited-time offers, and flash sales to create a sense of urgency and curiosity, enticing customers to make impulsive buying decisions.
Understanding consumers’ buying habits from an emotional standpoint is key in retail marketing. By playing on customers’ emotions and leveraging cognitive biases, retailers can optimize their check-out process, deploy attention-grabbing product packaging, and utilize captivating visual merchandising techniques to encourage impulsive purchases.
Whether it’s through strategic product placement or attention-grabbing in-store displays, brick-and-mortar retailers exploit cognitive biases to capture customers’ attention and create the desire for instant gratification. Online retailers, on the other hand, rely on persuasive online visuals, user-friendly platforms, and personalized recommendations to target consumers’ cognitive biases and drive impulsive buying.
Retail therapy, a psychological concept rooted in emotional shopping, is another facet of impulse buying that is heavily influenced by cognitive biases. By capitalizing on consumers’ desire for emotional satisfaction, retailers utilize promotions and sales to lure customers into making impulsive purchases, turning retail therapy into a powerful marketing tool.
In conclusion, cognitive biases significantly impact consumer behavior when it comes to impulse buying. Effective retail marketing strategies leverage these biases to optimize the purchase decision-making process, create an emotional connection with consumers, and drive impulsive purchases, ultimately shaping the latest retail trends.
The Role of Social Interactions in Impulse Buying
Social interactions play a significant role in impulse buying, a phenomenon that has become increasingly prevalent in today’s society. Retail therapy, the act of shopping as a way to improve mood, often involves social interactions. Whether it’s shopping with friends, seeking advice from family members, or sharing purchase experiences on social media, these interactions can greatly influence consumer behavior.
Product packaging and emotional shopping also contribute to the impact of social interactions on impulse buying. Retail marketing strategies, such as visual merchandising and product placement, are designed to grab the attention and trigger emotions in consumers. When these strategies are combined with social interactions, individuals may feel the need to conform to their peers’ buying habits or seek instant gratification through impulsive purchases.
Consumer research has shown that the check-out process can be a key moment for impulse buying. This is especially true in the era of online shopping, where consumers are exposed to various sales promotions during the purchase decision process. Social interactions, such as reading reviews or seeking recommendations from others, can further influence the final purchase decision by reinforcing or challenging the consumer’s initial intentions.
Another factor that impacts impulse buying is price strategy. Social interactions can play a role in the perception of product value and affordability. Comparisons between friends or social media acquaintances may lead to impulsive purchases as individuals strive to keep up with the latest retail trends.
In conclusion, social interactions have a significant impact on impulse buying. Whether it’s through in-store shopping experiences or interactions on social media, these interactions can influence consumer behavior and contribute to the allure of instant gratification. Understanding the role of social interactions in impulse buying can help retailers tailor their marketing strategies and better satisfy the needs and desires of consumers in the evolving world of ecommerce.
The Effect of Advertising and Marketing Strategies on Impulse Buying
In today’s world of consumer behavior, where online shopping has become increasingly popular, advertising and marketing strategies play a crucial role in influencing impulse buying. Companies employ various tactics, both online and in brick-and-mortar stores, to capitalize on the psychological tendencies of consumers.
One powerful tool that marketers use is product packaging. The design and visual appeal of a product’s packaging can create a sense of desire and urgency in consumers, pushing them to make impulsive purchases. In the world of ecommerce, where consumers cannot physically touch and feel the products before buying, attractive packaging can make a significant impact on impulse buying.
Emotional shopping is another aspect that marketers tap into. By understanding the shopping psychology of consumers, companies can create advertisements and marketing campaigns that trigger particular emotions, such as joy, excitement, or nostalgia. These emotions can increase the likelihood of impulse buying, as consumers seek instant gratification and a sense of happiness through their purchases.
Moreover, retail trends play a crucial role in influencing impulse buying. Companies invest in consumer research to stay updated on the latest retail trends. This information helps marketers strategically place products and create a conducive environment for impulse buying. From product placement to price strategy to visual merchandising, every aspect of retail marketing is carefully crafted to encourage customers to make spontaneous purchases.
The check-out process and sales promotions also have a significant effect on impulse buying. Retailers design their check-out process to maximize exposure to tempting products, such as candies or small accessories placed near the cash register. Additionally, sales promotions and limited-time offers create a sense of urgency and excitement, driving consumers to make impulsive purchase decisions.
Lastly, retail therapy, or the act of shopping to improve one’s mood or alleviate stress, is a common motivator for impulse buying. Advertising and marketing strategies often target consumers who are seeking an emotional boost through shopping. By positioning their products as a form of retail therapy, companies can encourage impulse buying among customers.
In summary, advertising and marketing strategies have a profound impact on impulse buying. By leveraging consumer psychology, understanding retail trends, and employing various tactics such as product packaging, emotional shopping appeals, and strategic placement, companies can influence purchasing decisions and drive impulse buying behavior among consumers.
The Influence of Store Layout and Design on Impulse Buying
The layout and design of a store significantly impact consumer behavior, particularly when it comes to impulse buying. Consumer research has shown that certain elements of store layout and design can increase the likelihood of impulse purchases and influence the purchase decision process.
One important factor that affects impulse buying is product placement. Retailers strategically position products to catch the attention of shoppers, placing high-profit or popular items at eye level or near the entrance. Additionally, attractive product packaging and creative displays can entice shoppers to make spontaneous purchases.
Another influential factor is the store’s sales promotions and price strategy. Limited-time offers, discounts, and special deals can create a sense of urgency and encourage impulse buying. Consumers may feel compelled to take advantage of a good deal or fear missing out, leading them to make impulsive purchases.
While online shopping has become increasingly popular, in-store shopping still offers unique advantages for impulse buying. The ability to touch, feel, and try on products can evoke an emotional response and contribute to instant gratification. Moreover, the check-out process, strategically placed near enticing displays or impulse buy items, can prompt consumers to add more items to their purchase.
The phenomenon of “retail therapy” also plays a role in impulse buying. Retail marketing often taps into consumers’ desire for emotional satisfaction and stress relief through shopping. The store environment, including music, lighting, and ambiance, can be carefully curated to enhance the emotional appeal and encourage impulse purchases.
As retail trends continue to evolve, so do consumers’ buying habits. Ecommerce has opened up new opportunities for impulse buying, with personalized product recommendations, one-click purchases, and targeted advertisements. Additionally, consumer behavior research is continually being conducted to understand and optimize the influence of store layout and design on impulse buying.
In conclusion, the layout and design of a store can have a profound impact on consumers’ impulse buying behavior. Product placement, sales promotions, price strategy, and an appealing store environment all contribute to increasing the likelihood of spontaneous purchases. By understanding shopping psychology and the factors that influence impulse buying, retailers can effectively shape the shopping experience and boost their sales.
The Relationship Between Impulse Buying and Self-Control
Impulse buying refers to the spontaneous purchase of goods or services without prior planning or consideration. It is often triggered by various factors, including visual merchandising, product packaging, price strategy, and emotional shopping. The rise of online shopping and sales promotions in ecommerce has further influenced impulse buying behavior.
One significant aspect of impulse buying is the lack of self-control. Consumers who engage in impulse buying often struggle with resisting immediate gratification and controlling their impulses. This can lead to impulsive purchase decisions that may not align with their long-term financial goals.
In-store shopping experiences play a crucial role in stimulating impulse buying behavior. Retailers employ various retail marketing strategies, such as product placement and attractive displays, to entice consumers and encourage impulse purchases. Consumer research has shown that certain colors, sounds, and scents can trigger impulsive buying behavior.
Self-control plays a vital role in managing impulse buying tendencies. Developing self-control skills can help individuals resist the allure of impulsive purchases and make more rational decisions. Practicing self-control involves setting personal financial goals, creating a budget, and avoiding impulsive buying triggers.
Retailers can also contribute to promoting self-control among consumers by improving the check-out process. By implementing a delay in the purchase process, such as adding additional steps or asking for confirmation, retailers can give consumers the opportunity to reconsider their purchase decision and potentially resist the impulsive urge.
Understanding the relationship between impulse buying and self-control is essential for both consumers and retailers. Consumers can benefit from recognizing their impulsive tendencies and developing strategies to enhance self-control. Retailers can leverage this knowledge to create retail environments that balance consumer desires for instant gratification with responsible shopping habits. By aligning retail trends and retail therapy with consumer behavior research, retailers can create a shopping experience that satisfies both emotional needs and long-term financial goals.
Impulse Buying as a Form of Instant Gratification
Impulse buying is a common phenomenon that occurs in the context of online shopping, where consumers make unplanned purchases on a whim. It is often triggered by sales promotions and discounts that create a sense of urgency and excitement in consumers, driving them to make impulsive purchase decisions.
One of the reasons why impulse buying is so prevalent in online shopping is the convenience and ease of the check-out process. With just a few clicks, consumers can complete their purchase without much thought or consideration. This makes it easy for them to succumb to impulsive buying habits and make purchases they may not have otherwise made.
Retail marketing strategies, such as strategic product placement and persuasive visual merchandising, also contribute to impulse buying. Online retailers carefully arrange their products and use attention-grabbing visuals to entice consumers to make impulsive purchases. This taps into consumers’ desire for instant gratification, as they get a sense of satisfaction and pleasure from making spontaneous purchases.
Ecommerce has also played a significant role in the rise of impulse buying. Consumers can now shop anytime, anywhere, and with just a few taps on their mobile devices. This easy accessibility to retail therapy fuels impulsive buying, as consumers can satisfy their desires for instant gratification without having to physically visit a store.
Retail trends and consumer behavior research have shown that emotional shopping is another driver of impulse buying. Consumers may use shopping as a way to cope with negative emotions or to reward themselves. This emotional connection to shopping leads to impulsive purchases, as consumers seek immediate satisfaction and gratification.
In response to these findings, retail businesses have adapted their price strategies to encourage impulse buying. They strategically offer limited-time sales or limited-quantity promotions that create a sense of urgency and scarcity. This taps into consumers’ fear of missing out and further drives them to make impulsive purchases.
In conclusion, impulse buying is a form of instant gratification driven by various factors in online and in-store shopping. It is influenced by retail marketing strategies, consumer behavior, and the desire for immediate satisfaction. Understanding the psychology behind impulse buying can help both retailers and consumers make more informed decisions in their shopping experiences.
The Link Between Impulse Buying and Consumer Satisfaction
In the world of ecommerce and online shopping, impulse buying has become a key factor in consumer satisfaction. It is a phenomenon that occurs when a consumer makes a purchase decision on a whim, without prior planning or deliberation. This type of buying behavior is often driven by a variety of factors, including product packaging, product placement, price strategy, and the check-out process.
One of the main reasons why impulse buying leads to consumer satisfaction is the concept of retail therapy. Many individuals find comfort and enjoyment in the act of shopping, which can provide a temporary escape from stress or negative emotions. Retail therapy taps into the psychology of emotional shopping, offering instant gratification and a sense of reward.
Visual merchandising plays an important role in encouraging impulse buying and subsequently increasing consumer satisfaction. Retail marketers strategically arrange products in a way that appeals to the senses and triggers impulse purchases. This can include eye-catching displays, limited-time sales promotions, and creative product placements.
Consumer research on buying habits has shown that impulse buying is also influenced by retail trends. As consumers are exposed to new products and trends, they are more likely to make spontaneous purchases. Retailers leverage this knowledge to stay ahead in the market, constantly updating their offerings to capitalize on consumer preferences.
Overall, the link between impulse buying and consumer satisfaction highlights the importance of understanding consumer behavior in retail marketing. By catering to consumers’ desire for instant gratification and providing an enjoyable shopping experience, retailers can enhance customer satisfaction and cultivate loyalty.
The Connection Between Impulse Buying and Retail Therapy
Impulse buying, a common phenomenon in consumer behavior, is deeply intertwined with the concept of retail therapy. Understanding the connection between these two can shed light on the motivations behind certain buying habits and shopping psychology.
Retail therapy refers to the practice of engaging in shopping as a way to improve one’s mood or emotional state. It is often seen as a form of self-soothing or instant gratification. Impulse buying, on the other hand, involves making unplanned purchases without much thought or consideration.
The retail environment plays a crucial role in encouraging impulse buying. Visual merchandising, clever product packaging, and strategic product placement can all influence consumers’ purchase decisions. Sales promotions and price strategies are also integral in capturing the attention of shoppers and enticing them to make impulsive purchases.
Retail trends have also had an impact on impulse buying. The rise of ecommerce and online shopping has made it easier than ever for consumers to make quick and impulsive purchases with just a few clicks. On the other hand, in-store shopping still offers the immediate gratification of being able to take the item home right away.
Research has shown that the check-out process is a prime opportunity for retailers to capitalize on impulse buying. By strategically placing items near the cash register, retailers can take advantage of consumers’ last-minute impulses to add something to their cart.
Retail marketing strategies continue to evolve and adapt to consumer research, seeking to understand and capitalize on the psychology behind impulse buying. Retailers are constantly exploring new ways to tempt consumers into making impulse purchases, from creating a sense of urgency through limited-time offers to leveraging the power of social proof and influencer marketing.
Understanding the connection between impulse buying and retail therapy can not only provide insights into consumer behavior but also guide retailers in designing effective strategies to capitalize on this phenomenon. By leveraging the psychology behind impulse buying, retailers can enhance the overall shopping experience and drive increased sales.
The Psychological Consequences of Impulse Buying
Impulse buying has become a common phenomenon in today’s society. As consumers, we are often tempted to make unplanned purchases, giving in to the momentary excitement of retail therapy and the instant gratification it brings. However, this behavior can have serious psychological consequences that go beyond the fleeting pleasure of a shopping spree.
Retail trends and shopping psychology play a significant role in encouraging impulse buying. The check-out process, for example, strategically places products that trigger impulsive desires, taking advantage of our subconscious decision-making. Product placement and visual merchandising in stores and online shopping platforms are carefully designed to entice consumers to make impulse purchases.
Consumer research shows that sales promotions and discounts also contribute to impulse buying. When faced with limited-time offers or special deals, our rational thinking often takes a backseat to our desire for instant gratification. In addition, the emotional aspect of shopping and the positive associations we have with certain products or brands can play a significant role in influencing our purchase decisions.
Ecommerce and online shopping have further amplified impulse buying tendencies. With just a few clicks, we can quickly make impulsive purchases without physically seeing or touching the product. The ease of online shopping, combined with targeted retail marketing techniques such as personalized recommendations and tailored advertisements, make it even harder to resist the urge to make impulse purchases.
While impulse buying can provide temporary satisfaction, it can also lead to negative consequences. Buying habits driven by impulse can result in financial strain, as overspending can quickly add up. Moreover, the emotional high that comes with impulse buying is often short-lived, leaving consumers feeling regret and guilt over their impulsive purchases.
In conclusion, impulse buying has become deeply ingrained in our consumer behavior due to various psychological factors. It is important for individuals to be aware of the consequences of impulsive spending and develop strategies to better manage their shopping habits. By understanding the psychology behind impulse buying, consumers can make more rational purchase decisions and avoid the negative effects of emotional shopping.
Strategies to Resist Impulse Buying
Resisting the urge to engage in impulse buying can be challenging, especially in today’s consumer-driven society. However, there are several strategies that individuals can employ to resist the allure of instant gratification and make more thoughtful purchasing decisions.
One effective strategy is to consciously slow down the check-out process. By taking a few moments to pause and reflect before making a purchase, individuals can give themselves the opportunity to reconsider whether they truly need or want the item. This simple act of delaying the purchase can help reduce impulse buying tendencies.
Avoiding sales promotions and retail therapy sessions can also be beneficial in resisting impulse buying. Retailers often use various techniques, such as limited-time offers and discounts, to encourage impulse purchases. By consciously avoiding these sales promotions, individuals can reduce the temptation to make impulsive and unnecessary purchases.
In today’s digital age, ecommerce has become increasingly popular, offering individuals the convenience of shopping from the comfort of their own homes. However, this can also contribute to impulse buying tendencies, as online retailers often use persuasive tactics to drive purchases. One way to resist this temptation is to create a wishlist of desired items and revisit it after a few days. This allows individuals to evaluate whether they still truly want the item or if it was just an emotional shopping impulse.
Retail marketing strategies, such as visual merchandising and product placement, are designed to entice consumers into making impulse purchases. By being aware of these tactics, individuals can become more conscious of how their buying habits are influenced and make more intentional decisions. Similarly, paying attention to product packaging and being critical of its impact on purchase decisions can help individuals resist the temptation of impulse buying.
Consumer research and staying updated on retail trends can also be helpful in resisting impulsive purchases. Underst